Association Between Breastfeeding Practices With Food Security Status
In this extremely disadvantaged population breastfeeding practices had rates relatively high than. Exclusive breastfeeding EBF is emphasized by the World Health Organization WHO as the most desirable way of infant feeding in the first 6 months.

Voices Of The Hungry Food Insecurity Experience Scale One Metric For The World Food Insecurity Insecure Inforgraphic
Severe moderate and mild food insecurity and food secure reference group.

Association between breastfeeding practices with food security status. Neither breastfeeding nor most complementary feeding practices UNICEF Regional Office for South Asia differed by socioeconomic status but children in the highest two fifth of a wealth index had 78 13469 and 53 11252 times greater odds than children in the lowest fifth of meeting minimum dietary diversity criteria. In upper-middle-income countries including Mexico maternal employment has been negatively associated with breastfeeding duration. We conducted a cross-sectional study including 847 children from 20 Primary Health Units.
Compared to other food groups vegetable intakes are lowest relative to recommendations. We examined mean duration of continued. Cross-sectional study of secondary.
Breastfeeding and initial introduction to vegetables may help infants establish long-lasting taste preferences. Association between Breastfeeding Practices and Nutritional Status of Children Aged 6-24 Months in Jessore Bangladesh. The aim of this study was to examine factors influencing EBF with emphasis on household food security status and maternal mental health.
The two primary economic factors that influence breastfeeding practices are employment status and income. Associations between childrens nutritional status and the study variables were assessed considering the following categorization of variables. Despite increasing numbers of women entering the workforce and disproportionately participating in.
Both breastfeeding and responsive feeding confer protective effects for the association between low attachment security and overeating among young children. Family food-security status was estimated using the Household Food Insecurity Access Scale and classified into. Effect of Prenatal and Postpartum Food Security Status on Breastfeeding Initiation and Duration in Massachusetts WIC Participants 20012009.
Exclusive breastfeeding rates are low in Canada. There is limited evidence of the association between breastfeeding feeding practices and stunting in indigenous children. Scholars have identified a dose-response association between breastfeeding duration and reduced risk for child morbidity and mortality.
General breastfeeding was assessed by asking the mother Was your child ever breastfed For mothers who replied no children were categorized as never breastfed Next mothers who replied. Exclusive breastfeeding rates are low in Canada. Each of these factors affects household food security but in different ways.
We collected information about the place and mode of delivery and professional breastfeeding. It would assist in identifying gaps in information that would encourage research into these areas. This study aimed to analyze the prevalence of breastfeeding and complementary feeding practices and explore their association with stunting in Ecuadorian indigenous children under two years of age.
This study provides new knowledge about associations between any breastfeeding in homeless families and the mothers cultural origins as well as her demographic and socioeconomic factors an understudied though increasing vulnerable population. It was also in agreement with a study done in Akransas which showed that mothers who had more knowledge were able to have the correct initiation as well as continued breastfeeding Moore. Giving only breast-milk to the infant directly from the breast or expressed and nothing else to drink or eat with the exception of vitaminmineral supplements or medicines within the previous 24 hours.
There was no significant association between maternal knowledge and breastfeeding initiation. Associations between maternal BMI breastfeeding practices and infant anthropometric status in Colombia. 18 Non-exclusive breastfeeding was defined as having given breast-milk.
Request PDF On Mar 1 2006 Ana Claudia Zubieta and others published Breastfeeding practices in US households by food security status Find read. We examined the relationship between breastfeeding and initial vegetable introduction and vegetable intake in early childhood ages 1360 months. Unfortunately a breastfeeding paradox exists where infants of low-income families who would most gain from the health benefits are least likely to breastfeed.
This paper is a first attempt at bringing all facts about breastfeeding and its relationship to food security and sustainable goals together in one document. Child age and gender were obtained from the face-to-face interview. Our aim was to identify feeding practices and to evaluate the association between breastmilk intake and complementary feeding focusing on ultra-processed foods UPF and sweetened beverages among children under 2 years old.
We explored the relation between household food insecurity status and the continuation of any breastfeeding after early cessation of exclusive breastfeeding defined here as cessation before 6 mo among the subset of women who began breastfeeding but ceased exclusive breastfeeding before 6 months. Solving household food insecurity and. It is noted that in the writing of the world breastfeeding trends.
Mothers who do not breastfeed may struggle with responsive feeding given inexperience with attending to childrens hunger and satiety cues. EBF has beneficial health effects on mothers and infants. Secondary analysis of ENSIN 2010 springermedizinde Skip to main content Registrieren Login Mein Profil.
Low rates of EBF given possible protection of. The linked study did show an association between food insecurity and the duration of exclusive breastfeeding. Anemia nutritional status and breastfeeding practices among mother-child pairs in vulnerable areas of Greater Beirut Lebanon - Volume 79 Issue OCE2 Skip to main content Accessibility help We use cookies to distinguish you from other users and to provide you with a better experience on our websites.
Exclusive breastfeeding was defined according to the WHO indicator for IYCF practices ie. Breastfeeding fulfills food security criteria by providing the infant access to sufficient safe and nutritious food that meets dietary needs and food preferences. This was in agreement with the findings of a study conducted in Tanzania Exavery et al 2015.
The linked study did show an association between food insecurity and the duration of exclusive breastfeeding. Almost half of women in food-insecure households had ceased exclusive breastfeeding after two months whereas half of the women in food-secure households breastfed exclusively for at least four months. Almost half of women in food-insecure households had ceased exclusive breastfeeding after two months whereas half of the women in food-secure households breastfed exclusively for at least four months.
For example women who are employed may have higher food security due to their income but tend to spend less time with infants making EBF difficult to maintain.
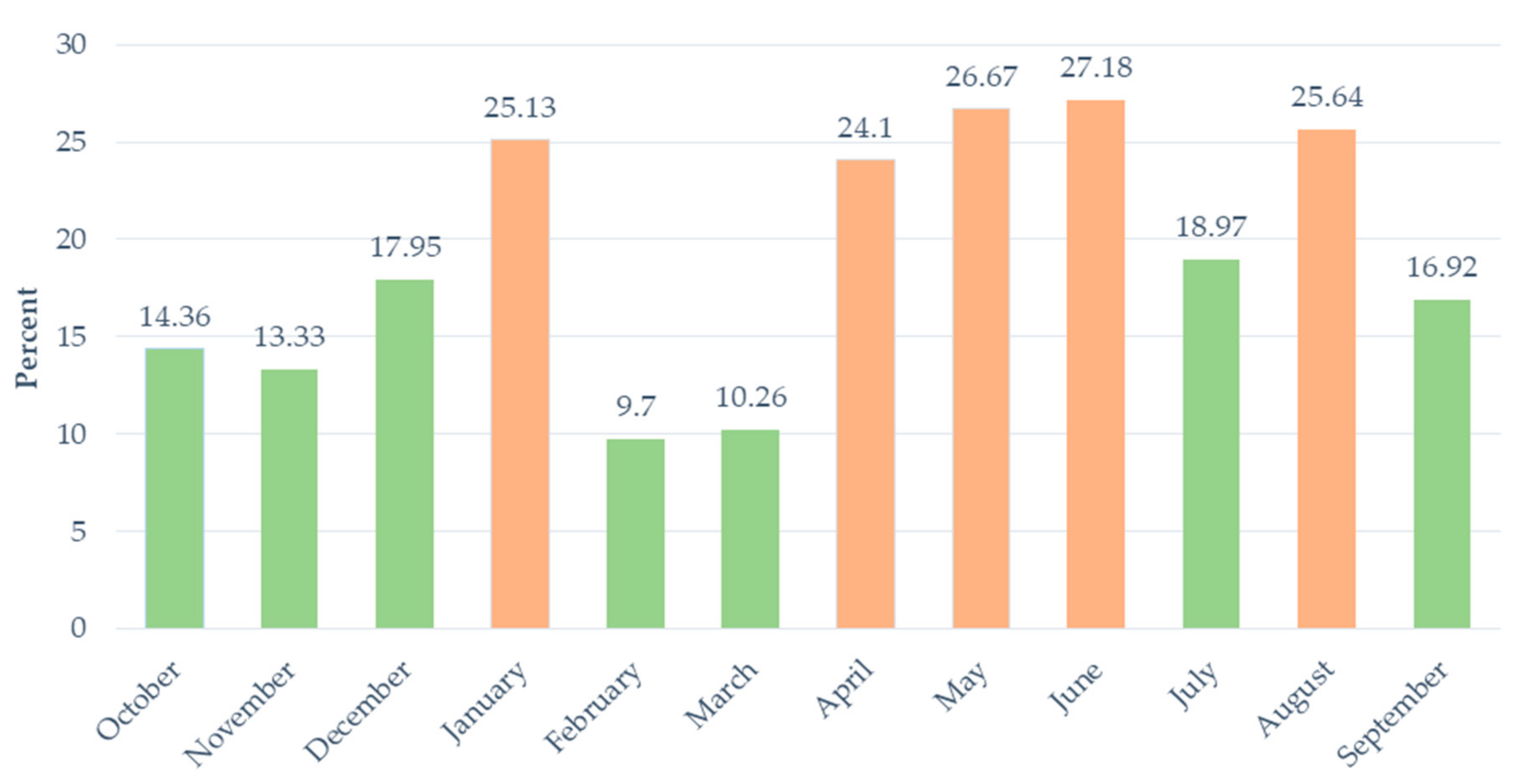
Nutrients Free Full Text Seasonal Food Insecurity Among Farm Workers In The Northern Cape South Africa Html

Foods Free Full Text Food Security And Sustainability Discussing The Four Pillars To Encompass Other Dimensions Html

Foods Free Full Text Food Security And Sustainability Discussing The Four Pillars To Encompass Other Dimensions Html

Conceptual Framework Of Factors That Influence Infant Feeding Practices Download Scientific Diagram

Pdf The Role Of Breastfeeding Protection Promotion And Support In A Developing World

Relation Between Household Food Insecurity And Breastfeeding In Canada Food Insecurity Relatable Breastfeeding




Posting Komentar untuk "Association Between Breastfeeding Practices With Food Security Status"